Varicose Veins : Symptoms, Causes, Types, Complications, Risks and Treatment
Have you ever noticed blur or purple-colored dark veins on your body, especially the lower body? Have you ever wondered what these veins are and what caused their sudden appearance? If you are concerned with the appearance of these dark blue- or purple-colored veins, then you don’t need to worry. These veins are called Varicose veins. In this blog, we will explore more about varicose veins and learn in detail about their causes, symptoms, stages, diagnosis, complications, prevention, treatment, and more. So, stay with Dr.Care Homeopathy till the end, as we learn together about varicose veins.
Varicose veins Definition:
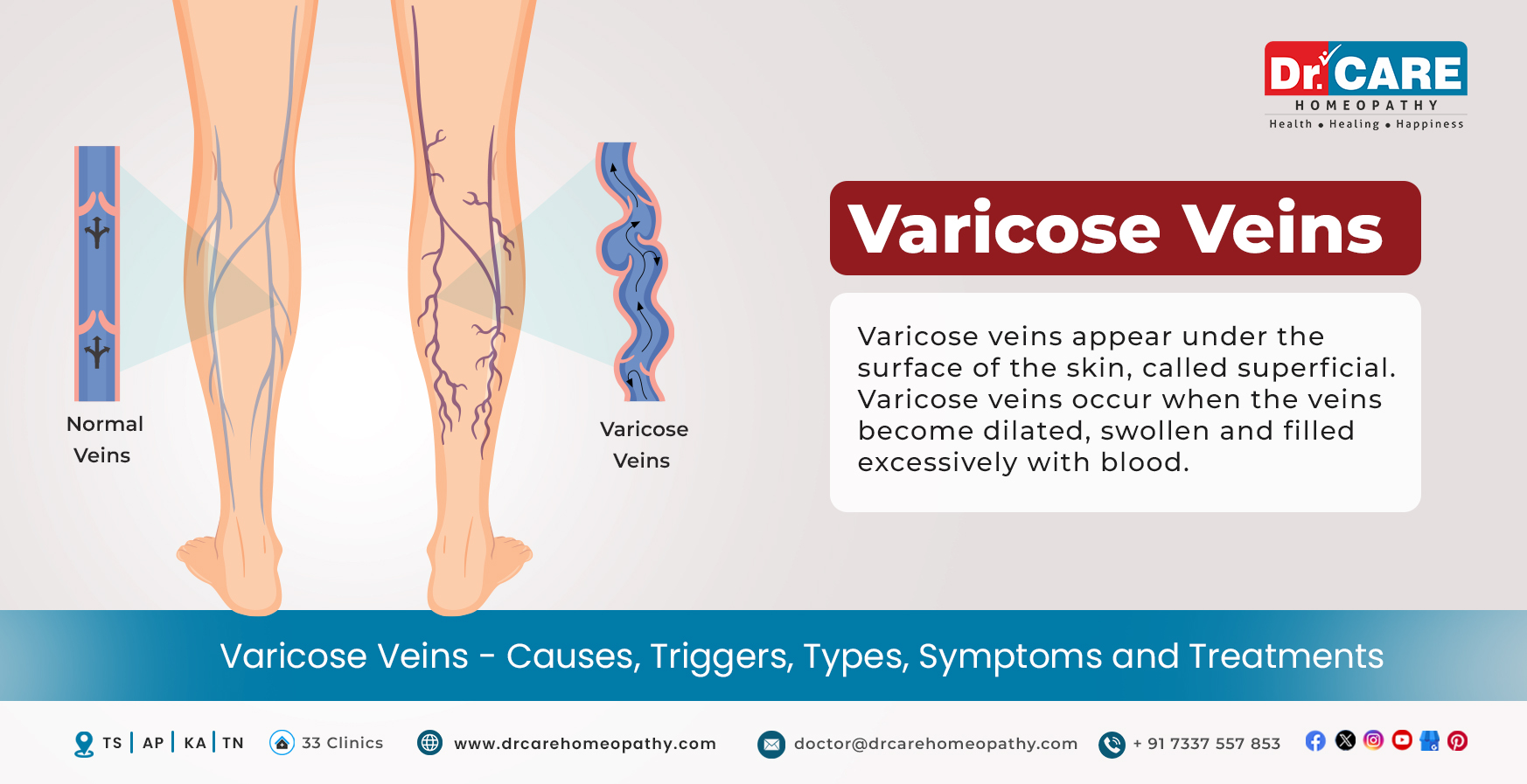
Varicose veins appear under the surface of the skin, called superficial. Varicose veins occur when the veins become dilated, swollen, and filled excessively with blood. These veins can appear anywhere on the body and are commonly seen in the lower body.
How are Varicose Veins Formed?
When the walls of the veins become weak and the valves don’t function properly, varicose veins begin to form on the skin. As a result of improper valve functioning, blood starts to build up in the veins. This gives the veins a swollen, raised, and blue or purple-colored appearance. Varicose veins are also called varicosities or varicoses.
Reason for varicose veins:
Varicose veins are a common problem and occur when the valves and walls of the veins become weak or damaged. Veins have one-way valves within them. These valves open and close to maintain the flow of blood towards the heart. When the veins become weak or damaged, the blood starts accumulating and even flowing backward in the veins (reflux). As a result of this blood pooling, the veins become enlarged and distorted; thus, varicose veins are formed.
Types of varicose veins:
There are various types of varicose veins. These veins affect the superficial system of veins. While these varicose veins, in most instances, are not life-threatening, they can still cause pain and discomfort in some cases, thereby affecting their daily life. Determining the type of varicose veins is essential to understanding its underlying cause and treatment with the right treatment approaches.
The different types of varicose veins include the following,
1) Telangiectasia varicose veins:
Telangiectasia varicose veins are known as spider veins. The most common type of varicose veins is similar to a spider web on the skin. The color of these veins ranges from red-blue to purple.
Telangiectasia varicose veins appear on the legs, ankle, and face. This type of varicose vein occurs when the blood vessels present near the skin broaden and form a web-like appearance. Individuals with telangiectasia varicose veins may experience symptoms of discomfort, pain, and itching on the skin.
2) Saphenous varicose veins :
Saphenous varicose veins are called Trunk varicose veins. These varicose veins are thick, knobbly looking and affect the legs. Saphenous veins are the major superficial and longest veins related to varicose veins in the body. This vein starts at the ankle and moves up to the groin region.
Saphenous varicose veins happen when the valves of the vein fail to function properly, leading to blood flowing backward toward the ankle or pooling together. As a result, the veins become bulged and distorted, pushing up against the skin. Saphenous varicose veins are unappealing as they become evident on the skin. In some cases, they may appear on the skin present above the vein in the form of red or brown patches. Individuals with this type of varicose veins may experience pain, itching, discomfort, and cramping in the area affected.
3) Reticular varicose veins:
These varicose veins are usually red and clustered together like a network. This type of varicose veins spreads like a mesh and takes up more area on the skin compared to telangiectasia varicose veins. Reticular varicose veins are a more prominent type of varicose veins and are typically observed on the ankles, back of the knees, and inner thighs. Individuals having Reticular varicose veins often experience cramps and pain in their lower legs.
4) Pregnancy-Related Varicose Veins
Pregnant women produce an extra amount of blood that adds extra pressure on the blood vessels, especially on the legs. This excessive pressure leads to the formation of varicose veins on the legs and the pelvic area. Additionally, women who have had multiple past pregnancies are also susceptible to developing a condition called Pelvic Congestion Syndrome or PCS. PCS leads to the formation of moderate to severe varicose veins in the pelvis region and the legs. The varicose veins in pregnancy are typically more painful than the traditional ones.
Difference Between Varicose veins vs Spider veins
Varicose veins and spider veins are commonly occurring vascular conditions that affect the veins, especially in the legs. While both are mostly similar and have similar causes, there are certain differences setting them apart. The various differences between varicose veins and spider veins include the following,
| S.No | Varicose Veins | Spider Veins |
|
|
Varicose veins are twisted, large, knobbly, and swollen veins. | Spider veins are similar to varicose veins. However, they are smaller in size and appear closer to the surface of the skin. |
| 2. | Varicose veins are usually dark bluish or purple. | Spider Veins are mostly red or blue and look similar to spider webs or tree branches. |
| 3. | Varicose veins are often present beneath the skin. | Spider Veins Are smaller and are seen more on the superficial skin. |
| 4. | Varicose veins may cause symptoms such as pain, swelling, cramping, fatigue, and heaviness in the legs. | In most cases, spider veins are asymptomatic. However, in some cases, it may cause mild itching or burning in the affected area. |
Difference Between Deep Vein Thrombosis (DVT) vs. Varicose Veins
Deep wind thrombosis and varicose winds are both conditions that affect the veins. However, these two conditions have a lot of differences. This includes the veins affected, symptoms, and also the causes. The differences between deep vein thrombosis (DVT) and varicose veins are given below,
| S.No | Deep Vein Thrombosis (DVT) | Varicose Veins |
| 1. | In Deep Vein Thrombosis (DVT), The veins affected are present deeper in the limb. | Varicose Veins affect the veins that are found near the surface of the skin. |
| 2. | Deep wind thrombosis is typically a very serious health condition that can also become life-threatening. | Varicose veins typically are not a very serious condition. |
| 3. | In deep wind thrombosis, blood clots form deep within the veins in the body, especially the legs. | In varicose veins, the veins become swollen, enlarged, and twisted and usually occur on the surface of the skin, especially in the legs. |
| 4. | Blood clots occurring in deep vein thrombosis can block the blood flow in the veins that are affected. | In varicose veins, damaged valves present in the veins can cause poor blood circulation. |
| 5. | The risk factors of developing (DVT) deep vein thrombosis include having a blood clotting disorder, a family history, obesity, pregnancy, taking birth control pills, and conditions such as cancer, heart disease, lupus, or infection. | The risk factors of varicose veins include a sedentary lifestyle, family history, being overweight, pregnancy, standing for longer period of time, sitting for prolonged durations, and frequent constipation. |
| 6. | The various symptoms of deep vein thrombosis may include swelling in the leg, redness on the skin in the area affected with clots, pain and tenderness, and skin that feels warm to the touch. | The symptoms of varicose veins may include bulging, twisted, and raised blue- or purple-colored veins that can cause itching and sometimes pain and discomfort. |
| 7. | Deep vein thrombosis requires immediate medical attention upon experiencing the symptoms. | Varicose veins and its symptoms do not require immediate medical attention. |
Varicose veins stages:
While varicose veins are usually harmless, if left untreated, they can progress from a symptomatic problem to a serious health condition. Varicose veins usually develop in stages, and by the time the individual realizes the presence of varicose veins, the condition has already progressed into the advanced stages. Hence, it is essential to identify the stages of varicose veins to seek proper treatment and manage the problem effectively. The stages of varicose veins include the following,
Stage 1: Spider Veins
In this stage of varicose veins, small blood vessels lying close to the skin’s surface dilate. This eventually leads to the development of spider veins. The dilated capillary vessels and veins are also known as telangiectasias. Spider veins in most instances, do not cause any symptoms or discomfort, but they may cause mild burning and itching in the area affected. These veins are usually seen on the legs; however, they may appear anywhere on the body.
Stage 2: Enlarged Varicose Veins
The stage 2 of varicose veins is characterized by the presence of more evident enlarged veins. These veins cause pain and discomfort and have a blue or purple-colored appearance. Enlarged varicose veins also look bulged or twisted and are seen mostly on the legs. These veins cause a heavy feeling in the legs, especially after the individual has been standing or sitting for a prolonged time.
Stage 3: Edema without any skin changes
The stage 3 of varicose veins is characterized by edema in the legs and ankles. Edema is a problem that arises when excessive fluid builds up within the tissues due to poor circulation. This causes the legs and ankles to swell. Edema can present in symptoms such as numbness, muscle cramps, pain, and itching in the areas affected. It is important for patients experiencing symptoms of edema to seek medical attention immediately before their condition worsens.
Stage 4: Changes in the skin
The stage 4 of varicose veins is characterized by changes in the skin. In this particular stage, leaking of blood from blood vessels into the skin tissue occurs due to prolonged edema and poor blood circulation. As the condition progresses, the skin starts to become darker with increased sensitivity to pain. In this stage, the skin becomes discolored and has a hard, leathery texture. This stage is characterized by reddish-brown skin discoloration along with redness, itchiness, and flakiness of the skin.
Stage 5: Ulcer formation
In this stage, untreated varicose veins turn into venous ulcers, which are open wounds. This stage is a common complication associated with chronic venous insufficiency. Individuals with venous ulcers may experience the presence of open sores on the skin, which are typically painful and take a long time to heal. These ulcers can also have a foul smell along with discharge.
Venus ulcers are caused when there is excessive pressure on the veins, leading to the leakage of fluid into the tissure from the blood vessels. As a result of the fluid buildup, The tissue becomes inflamed and damaged, making the process of healing difficult. In severe cases, the ulcers may get infected and may also lead to a potentially fatal condition called cellulitis.
Causes of varicose veins:
Varicose veins may typically form when the blood pressure within the veins increases, and the veins become weak. Some of the potential causes and varicose veins risk factors include the following,
- A family history of varicose veins
- Effect of hormones
- Excessive weight gain
- Pregnancy
- Being aged above 50
- Going through menopause
- Standing for longer time period
- Wearing tight-fitted clothes
- The habit of smoking
- Taking hormone replacement therapy
- Taking oral contraceptive medications
- A sedentary lifestyle.
Symptoms of varicose veins:
Individuals with varicose veins may present with the following symptoms,
- Leg heaviness: The muscles in the leg may feel heavy and fatigued. Heavy legs are common, especially after physical activity.
- Pain: The areas affected by varicose veins, especially the legs, may feel painful. The individual will also feel soreness and muscle cramps in some cases.
- Itchy skin: The skin and surrounding areas affected by varicose veins may be itchy.
- Bulging of veins: Individuals with varicose veins will have blue or purple-colored veins that are swollen and twisted appearing on their skin. These veins also look like ropes and can even appear in clusters. Varicose veins are often seen on the legs, feet, and ankles. These veins may be accompanied by small blue or red lines called spider veins.
- Edema (swelling): As a result of excessive buildup of fluid, swelling along with throbbing may occur on the legs, feet, and ankles.
- Discoloration of the skin: If not treated on time, the skin affected by varicose veins may become discolored. Typically, brown discoloration is seen on the skin.
- Ulcers: In severe cases of varicose veins, the individual may develop ulcers on the skin, which can be painful.
Early signs and symptoms of varicose veins:
Before the development of varicose veins, the person may notice a few symptoms indicating the beginning of varicose veins. The various early signs and symptoms of varicose veins to be aware of include the following,
- Swelling in the feet
- Pain in the legs, especially after prolonged walking or doing any other physical activity
- Leg cramps
- Unusual shining on legs
- The appearance of light red spots on the skin
- The appearance of dark veins on the surface of the skin
Varicose veins during pregnancy
Varicose veins develop due to poor blood flow, leading to the pooling of blood in the veins and making them bulge under the skin. Varicose veins in time of pregnancy are a common occurrence. At the time of pregnancy, a woman’s body experiences several hormonal changes along with weight gain, both of which play a role in the development of varicose veins.
Varicose wins during pregnancy can develop due to various reasons such as,
- Increased level of progesterone in the body
- Increased pressure on the pelvic region due to the baby’s weight causes a decrease in the blood flow in the pelvis and legs
- High volume of blood in the body
Complications of varicose veins:
In most cases, individuals with varicose veins experience no complications. However, in certain cases, the following complications may occur,
- Decreased blood circulation
- Deep vein thrombosis
- Thrombophlebitis (vein inflammation)
- Venous ulcers
- Swelling in legs
- Bleeding (rarely)
- Lipodermatosclerosis
- Varicose eczema
Diagnosis of Varicose veins:
One of the primary steps in varicose veins diagnosis is a physical examination. During a physical examination, the physician will check the patient for visual signs of varicose veins, such as swelling. For this, the patient will be asked to stand while the doctor does the physical examination. Additionally, the doctor will also ask the patient about their lifestyle, medical history, family history, and symptoms being experienced.
To confirm the presence of varicose veins and establish the underlying cause, the doctor will order further tests. These diagnostic tests may include the following,
1) Doppler test for varicose veins:
This test is a type of non-invasive technique that uses sound waves to check the blood flow through the vessels in the legs. This ultrasound test helps detect and establish the severity of varicose veins. Doppler test is one of the most commonly used diagnostic tests for varicose veins.
2) Schwartz tests varicose veins:
This test is used to confirm the presence of varicose veins. In this test, the lower leg, where the saphenous varicose vein is located, will be tapped with one hand to check for an impulse. In case an impulse is felt, it indicates that the valves present in the superficial venous system are not functioning normally.
3) Perthes test varicose veins:
This diagnostic test helps in differentiating the valvular insufficiency in the superficial venous system and the deep venous system.
4) Fegan’s test for varicose veins:
Fegan’s test is used for clinical examination to assess the presence of varicose veins. This is a method that helps in identifying varicose sites, especially in the lower limbs.
5) Trendelenburg Test for varicose veins:
This test helps in determining valve incompetence in individuals affected with varicose veins. This test is also called the Brodie-Trendelenburg test.
Prevention of varicose veins:
There are several measures that you can take to reduce your risk of developing varicose veins You can also speak to your physician or healthcare provider to learn about the different measures to take to prevent as well as treat your varicose veins problem. In general, the following measures can help in preventing varicose veins,
- Avoid standing for longer periods
- Avoid sitting for extended periods
- Avoid sitting with your legs crossed
- Get regular exercising done, such as walking and yoga
- Elevate your legs about the waist to improve the blood flow to your heart
- Quit tobacco and smoking
- Avoid wearing tight-fitted clothes
- Maintain a healthy weight by eating healthily
- Sleep or sit with the feet elevated with the help of a pillow
- Wear special stockings or compression socks
Varicose veins Treatment:
There are various treatment options available for treating varicose veins. These treatments are given depending on the condition of the patient, the severity of the disease, and the symptoms being experienced. In case the patient’s condition does not allow the patient to get definitive treatments, there are various conservative treatment options available to manage the condition and provide symptomatic relief to the patient.
The various conservative treatment options for varicose veins include,
- Healthy lifestyle modifications
- Using compression stockings
- Medicines
The various definitive treatment approaches used to treat individuals with varicose veins may include,
- Endovenous Laser Ablation Therapy
- Sclerotherapy
- LAFOS
- Microwave Ablation
- Radiofrequency Ablation
- MOCA
- The V-Block
- Varithena
- Steam
- Superglue
The treatment for varicose veins is based on the underlying cause. At Dr Care Homeopathy, we provide exceptional diagnostic services to determine the root cause of varicose veins. Based on the diagnosis, our team of best homeopathy specialists provides a personalized treatment plan to reduce the appearance of varicose veins and manage the condition and its symptoms.
Allopathy treatment can be used to treat varicose veins, but it has several side effects. Hence, many individuals with varicose veins opt for homeopathy treatment as it offers good results with minimal to no side effects. If you have varicose veins, then it is essential to show it to a homeopathy doctor to seek proper treatment. Our team of homeopathic specialists provides the best homeopathy treatment for varicose veins to ensure an improved overall quality of life. At Drcare Homeopathy, we give the best combination of lifestyle changes and homeopathic treatments to manage the condition of varicose veins effectively.
Homeopathic Medicine for Varicose Veins
Homeopathic medicine for varicose veins offers the best relief to the patient from its symptoms, such as pain and discomfort, and helps address any underlying cause. Homeopathic medicine for varicose veins offers a solution to the problem with minimal to no side effects. This holistic treatment approach is an effective way of treating the symptoms of varicose veins and enhances the appearance of the skin.
Conclusion
Varicose veins are a common condition affecting many individuals. While the condition may not be serious, it is always best to acknowledge the symptoms and get proper medical help to ensure optimal health. There are risk factors for this condition, such as a sedentary lifestyle and obesity, which, when addressed, can help reduce its risk. Individuals with varicose veins may experience mild pain, itching, and discomfort in the area affected.
At Dr Care Homeopathy, we have a team of renowned homeopathic doctors who provide the best homeopathic solutions for all conditions, including varicose veins. Our homeopathic specialists analyze a proper evaluation of the patient’s condition to provide the right diagnosis and formulate personalized treatment plans.
Frequently Asked Questions
5. How to identify varicose veins?
You can identify varicose veins through the following symptoms, Bulging bluish- or purple-colored veins A heavy feeling in the legs and feet Leg cramps Discoloration around the veins Skin itching A burning sensation around the area affected Swelling in the legs and feet Mild pain and discomfort in the legs
6. What are spider varicose veins?
Spider veins are similar to varicose veins. However, they are small and thin lines that are found closer to the surface of the skin. Spider veins are mostly red or blue in color and resemble spider webs. In most cases, these spider veins do not produce any symptoms. However, some patients may feel mild burning and itching in the area affected. Spider waves are mostly seen on the legs and feet. However, spider veins can still appear anywhere on the skin.
7. How to prevent varicose veins?
Varicose veins cannot be prevented completely. However, there are various ways through which its risk can be reduced. The various preventive tips to help reduce the risk fo varicose veins include the following, Managing underlying conditions Maintaining a healthy lifestyle Ceasing smoking Quitting tobacco Wearing loose-fitted clothes Avoiding standing or sitting for longer than usual
8. What is the outlook for individuals having varicose veins?
Varicose veins usually are not dangerous and don't cause any harm to the health in the long run. However, it is best to seek its treatment to reduce the risk of any future complications. Additionally, some people are concerned by the appearance of their affected skin, in such cases, seeking a doctor's guidance can help.
9. When should I go to the ER with varicose veins?
Call your emergency number immediately if you experience severe bleeding in your varicose vein.
 India
India UAE
UAE UK
UK United States
United States Dubai
Dubai






.png)