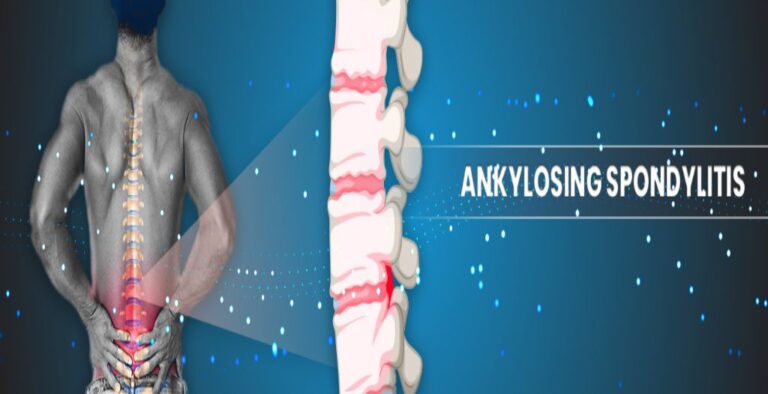
Spondylitis is a general term used to describe the group of chronic arthritis, such as a disease that affects the joints in the spine and sacroiliac region. Spondylitis is also known as spondyloarthritis. Various types of spondylitis affect various parts of the body. If not treated and managed on time, spondylitis can also cause other health problems. Joints, skin, digestive system, back, eyes, etc, are some common body parts that may be affected by spondylitis
What is Spondylitis:
Spondylitis is inflammation of the vertebrae (bones making up the spine). It is a general term used to describe the various conditions causing inflammation in the spine. Ankylosing spondylitis is the most commonly occurring form of Spondylitis.
Prevalence of Spondylitis:
A previous study from 2014 estimates suggests that between 0.1% and 1.4% of the global population were affected by ankylosing spondylitis (AS). It was also found that individuals with the gene HLA-B27 in their bodies were more at risk of developing ankylosing Spondylitis This ankylosing spondylitis is a type of spondylitis that leads to inflammation in the ligaments and joints in the spine.
Spondylitis Types:
There are two major categories through which spondylitis is categorized. As per the Spondylitis Association of America, there is an older traditional way of categorizing spondylitis, which contains 6 types of spondylitis, and A more recent classification divides all spondylitis diagnoses into two distinct categories.
There are a total of 6 types of spondylitis.
Ankylosing Spondylitis
Ankylosing spondylitis is the most commonly occurring type of Spondylitis. In this type of Spondylitis, the ligaments and joints of the spine become inflamed. This particular type of spondylitis can also affect the ankles, hips and knees. Lower back pain, stiffness, swelling and pain in the hip joint are some common symptoms of this type of spondylitis.
Psoriatic arthritis (PsA)
Psoriatic arthritis (PsA) is a type of Spondylitis that is an autoimmune condition causing inflammation in the skin, nails and joints. It resembles rheumatoid arthritis and can cause pain and swelling in the joints. Skin rashes (flare-up of psoriasis), swelling in between the joints of toes or fingers and pain, inflammation and swelling in the fingers, hands and feet are some common symptoms of this type of spondylitis.
Enteropathic arthritis (EnA)
It is a type of spondylitis that occurs along with IBD (inflammatory bowel disease). It is also known as enteropathic arthropathy. This condition causes inflammation and pain in the intestines. Some common symptoms of this type of spondylitis include severe diarrhea, pain in the joint, loss of weight and bloody bowels.
JuvenileSpondylitis (JSpA)
Juvenile spondylitis (JSpA) affects children and teenagers. In this type of spondylitis, the leg joints are usually g The common symptoms of this condition include pain in the areas joining the tendons, ligaments and muscles together, pain in the spine, etc.
Reactive arthritis
Reactive arthritis is also known as Reiter’s syndrome (ReA). In this type of spondylitis, the individual affected may experience pain in the peripheral joints, such as the knees and ankle. This type of Spondylitis occurs as a result of a bacterial infection. The bacterial infection may occur due to sexual transmission (chlamydia) or a gastrointestinal infection due to contaminated food (salmonella). Reactive arthritis is characterized by symptoms like pain in the spine, sacroiliac joint pain, swelling in the joints, eye inflammation, rashes on the skin, and inflammation in the genital area and bladder.
Undifferentiated Spondylitis
This particular type of spondylitis is called undifferentiated because it doesn’t fit the diagnostic criteria for ankylosing spondylitis or related conditions. If you have undifferentiated Spondylitis, you may not experience typical symptoms like pain in your back., digestive problems or skin rashes. Instead, your symptoms might include the following,
- Inflammation in the back
- Fatigue
- Inflammation in the eye
- Pain in the buttocks
- Dactylitis
- Enthesitis (heel pain)
- Peripheral arthritis
The new method of classifying spondylitis types
The new method of classifying the types of spondylitis focuses on the location in the body where it occurs. This system identifies two primary types of spondylitis, though some individuals may experience both types.
Axial Spondylitis
In this particular Spondylitis, the individual affected may experience symptoms in the back, hip or groin region. This group is categorized further based on whether the bone and joint changes are visible on X-rays or scans or if they are not detectable through imaging. The various types of axial Spondylitis may include the following,
- Psoriatic arthritis
- Enteropathic arthritis
- Reactive arthritis
- Ankylosing spondylitis
- Undifferentiated Spondylitis
- Peripheral Spondylitis
Peripheral Spondylitis
This particular type of Spondylitis includes various types of this condition that affect the arms and legs. The areas where the individual may experience symptoms in the joints include the following,
- Hands
- Wrists
- Shoulders
- Elbows
- Knees
- Ankles
- Feet
The different types of Spondylitis that fall into the category of peripheral Spondylitis include the following,
- Undifferentiated arthritis
- Enteropathic arthritis
- Psoriatic arthritis
- Reactive arthritis
Stages of Spondylitis:
The condition of spondylitis progresses through various stages. Every stage of spondylitis is characterized by different symptoms. Although the stages of spondylitis can vary based on the specific type of Spondylitis, they generally follow this progression pattern,
Early Stage
In the early stage, the individual affected with spondylitis often experiences the below symptoms,
- Pain and stiffness in the lower back
- Pain in the hips and groin area
The symptoms of Spondylitis in this stage may come and go.
Progressive Stage
In the progressive stage of Spondylitis, the symptoms become more prominent and can also start affecting other joints. The symptoms of this stage includes the following,
- Reduced mobility
- Joint stiffness, especially after rest
- The symptoms in this stage may become more persistent.
Advanced stage
In this stage, the affected individual may experience symptoms like,
- Severe inflammation in the joints may also cause damage
- Limited range of motion
In this stage, the patient may find it difficult to perform even the basic everyday tasks due to the limited range of motion in the back and hips.
Spondylitis Causes:
The exact causes of spondylitis diseases are not yet fully understood by doctors. However, medical research suggests that certain types, such as ankylosing spondylitis, may have a genetic factor playing a role. This means that individuals with a family history of the condition are at a higher risk of developing this condition.
Now, although the exact triggers of spondylitis are not very clear, researchers say genetics plays a significant role in the likelihood of developing these diseases. This makes family history an important factor when it comes to assessing the potential risk of this disease.
Research has identified up to 30 genes that may be associated with ankylosing Spondylitis. Additionally, some of these genes are also linked to other forms of Spondylitis. While genetics plays an important role, other potential causes include certain bacterial infections.
Individuals may be at an increased risk of developing types like enteropathic arthritis and reactive Spondylitis if they have a history of infections in areas such as the intestines, bladder, or genitals. These infections can act as triggers for inflammation, leading to the development or exacerbation of spondylitis symptoms.
The causes of Spondylitis may include the following,
Genetics: A predisposition due to specific gene variants, especially in families with a history of Spondylitis.
Bacterial Infections: Infections in the intestines, bladder, or genitals that increase the risk of developing certain types of Spondylitis.
You may also be at a higher risk of developing enteropathic arthritis if you suffer from other inflammatory bowel diseases (IBD), such as Crohn’s disease or ulcerative colitis. In fact, as per studies, up to 20 per cent of individuals with IBD also experience enteropathic arthritis, with the condition being more prevalent among teenagers and young adults.
Additionally, stress may also play a significant role in triggering or worsening certain types of spondylitis. A previous survey found that 80 per cent of people with ankylosing spondylitis reported that stress had a direct impact on their symptoms, highlighting the link between unmanaged stress and the aggravation of this condition.
What are the risk factors of spondylitis?
There are various risk factors of spondylitis. These risk factors that increase a person’s risk of developing spondylitis diseases include the following,
- Genetics
- Age
- Certain bacterial infections
- Having certain inflammatory conditions
- Spinal injuries due to accidents, physical labor or sports injuries
- Unmanaged stress
Spondylitis Symptoms
Every type of Spondylitis causes inflammation and pain. The most common symptom of pain is seen in the lower back. Depending on the type of Spondylitis you have, the symptoms you experience may differ.
Some common symptoms associated with Spondylitis include the following,
- Inflammation in the eye
- Fatigue
- Pain in muscles
- Pain in the joint
- Back pain
- Swelling in the legs and arms
Complications/Risks of Spondylitis:
The various Complications/Risks associated with Spondylitis include the following,
- Reduced Mobility: With time, severe inflammation due to Spondylitis may cause limited movement in the spine, hips, or other joints.
- Spinal Fusion: In severe cases, inflammation can lead to the fusion of vertebrae, which can cause loss of flexibility and a rigid spine.
- Heart problems: In some cases, individuals affected may develop heart problems such as inflammation of the aorta.
- Fatigue: Chronic inflammation and pain due to spondylitis can lead to constant fatigue and reduced quality of life.
- Breathing Difficulties: This complication can arise due to the fusion of the ribs and spine, which can restrict the expansion of the chest and reduce lung capacity, leading to breathing difficulties.
- Peripheral Arthritis: Inflammation may move to joints in the arms and legs, such as the shoulders, knees, or hips.
- Eye Problems: Uveitis, an inflammation of the eye, is a common complication of Spondylitis, leading to pain, blurred vision, and light sensitivity.
- Posture Changes: Advanced Spondylitis can cause a forward-stooped posture (kyphosis), especially in the upper back.
- Osteoporosis: Persistent inflammation can weaken bones, making them more prone to fractures.
- Digestive Problems: Inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) may occur alongside Spondylitis, leading to symptoms like abdominal pain and diarrhea.
- Neurological Issues: In rare cases, Spondylitis can cause compression of the spinal cord, leading to neurological problems such as numbness, weakness, or difficulty walking.
How is Spondylitis diagnosed?
To diagnose Spondylitis, your doctor will begin by conducting a thorough physical exam and discussing your medical history, including any family history of arthritis or autoimmune conditions. This helps identify potential symptoms and risk factors. In addition to the physical exam, several tests and imaging studies may be ordered to confirm the diagnosis,
Blood Tests
Inflammation Markers: Blood tests will check for elevated levels of inflammatory markers like C-reactive protein (CRP) and erythrocyte sedimentation rate (ESR). These indicate inflammation in the body, which is common in Spondylitis.
Signs of Infection: Blood tests also help rule out infections that can cause similar symptoms, ensuring the diagnosis focuses on inflammatory Spondylitis.
X-rays
Hip and Pelvis Imaging: X-rays of the hips and pelvis are used to look for early signs of joint damage or fusion in the sacroiliac joints, which is a hallmark of Spondylitis.
MRI Scans
Back, Hip, and Pelvis: MRI provides detailed images of the soft tissues, joints, and bones. This is particularly useful in detecting early signs of inflammation in the spine or sacroiliac joints that may not be visible on X-rays.
Genetic Testing
HLA-B27 Gene: A genetic test may be performed to check for the presence of the HLA-B27 gene, which is commonly associated with ankylosing Spondylitis and other forms of Spondylitis. While not everyone with Spondylitis carries this gene, it can be a strong indicator, especially in cases where the diagnosis is unclear.
These tests, combined with clinical findings, allow doctors to make an accurate diagnosis and develop an appropriate treatment plan.
Spondylitis Treatment:
Treatment for Spondylitis focuses on managing pain, reducing inflammation, and preventing further joint damage. Controlling inflammation in the spine, joints, and surrounding tissues can help alleviate symptoms and improve mobility. Some common treatment options that your doctor may recommend to treat Spondylitis include the following,
- Medications like NSAIDs (Non-Steroidal Anti-Inflammatory Drugs), Disease-Modifying Antirheumatic Drugs (DMARDs), Tumor Necrosis Factor-Alpha (TNF-Alpha) Blockers and TNF-alpha inhibitors.
- Steroid Injections
- Steroid Eye Drops
- Physical Therapy
- Gym-based exercises focusing on strength and flexibility
- Water therapy (aquatic exercises)
- Surgery such as Hip replacement surgery and Spinal surgery
Homeopathy treatment for Spondylitis
How does Homeopathic treatment help with Spondylitis?
Homeopathy offers a holistic approach to managing Spondylitis by focusing on alleviating symptoms and addressing the underlying causes of inflammation. Although it doesn’t cure Spondylitis, homeopathy can help reduce pain and improve the overall quality of life for individuals dealing with this condition. Homeopathy treatment for Spondylitis is individualized, and the treatment plan is created after considering various factors like the type of Spondylitis, the stage of the disease, the person’s specific symptoms, lifestyle, and constitution and the severity of the symptoms.
How Homeopathy Helps with Spondylitis Symptoms?
Homeopathy treatment provides symptomatic relief to patients with Spondylitis by addressing various symptoms. This includes,
Pain Management:
Homeopathic remedies focus on relieving chronic pain and stiffness that are commonly associated with Spondylitis. By reducing the intensity of pain, especially in the spine, lower back, and joints, individuals may experience greater comfort and mobility throughout the day.
Reducing Inflammation
One of the key benefits of homeopathy in the treatment of spondylitis is that is it also helps reduce inflammation in the joints and tissues. By targeting the inflammatory process, homeopathic remedies may help control the swelling and stiffness that spondylitis
Improving Mobility and Flexibility
Individuals with Spondylitis often experience limited movement due to joint stiffness and inflammation, and homeopathy remedies may help improve flexibility and relieve tightness in the affected areas. Over time, this can contribute to improved posture and mobility, reducing the risk of complications like spinal fusion.
Boosting Immunity
As Spondylitis is often associated to autoimmune issues, homeopathy treatment works by enhancing the body’s natural immune response. This not only helps in managing inflammation but also prevents the progression of the disease and reduces the frequency of flare-ups.
Alleviating Fatigue
Fatigue is a common symptom of Spondylitis, especially as the body struggles to cope with chronic inflammation. Homeopathy remedies support the body’s energy levels by addressing the underlying factors that contribute to fatigue, allowing individuals to feel more energized and less drained by the disease.
Managing Emotional and Mental Well-being
Spondylitis can have a significant impact on a person’s mental and emotional health due to chronic pain and limitations in daily activities. Homeopathy takes a holistic view, addressing emotional stress, anxiety, and depression that may accompany the condition. This can help improve overall well-being and promote a more positive outlook on managing the disease.
Benefits of Homeopathic Treatment for Spondylitis:
Homeopathy treatment offers several benefits to patients having spondylitis. Some of these benefits include the following,
Natural Approach: Homeopathy uses natural, non-invasive remedies that are free from synthetic chemicals. This makes it a gentle option for those who may be sensitive to conventional medications.
Personalized Treatment: Each treatment plan is made to meet the individual’s unique symptoms and constitution, ensuring that the approach is aligned with their specific needs and health status.
Fewer Side Effects: Homeopathic remedies generally have minimal or no side effects, making them a safer alternative for long-term management of Spondylitis.
Holistic Care: Homeopathy not only focuses on physical symptoms but also addresses emotional and psychological well-being, providing comprehensive care for individuals with spondylitis.
Homeopathic treatment can be a supportive option for managing spondylitis symptoms, especially when integrated with other lifestyle measures such as physical therapy and healthy habits. At Dr Care, our team of homeopathic specialists create individualized treatment plans to help you with various diseases, including Spondylitis. Our team focuses on providing long-term relief by addressing the root cause of the disease and not just the symptoms. We provide the best remedies after considering various patient-related factors to ensure they get the best treatment.
Conclusion
Spondylitis is a general term used to describe the group of chronic arthritis-like diseases affecting the joints in the spine and sacroiliac region. Depending on the type of Spondylitis you have, the symptoms you experience may differ. Pain and inflammation are common symptoms of Spondylitis. The treatment prescribed may also vary depending on the type of Spondylitis, the symptoms, the age of the patient, their lifestyle, etc.
Homeopathy treatment for Spondylitis offers the best solutions to those looking for long-term relief. At DrCare, we provide holistic care to our patients to help them get relief from various diseases, including Spondylitis. Our approach is highly patient-centric, with minimal to no side effects.