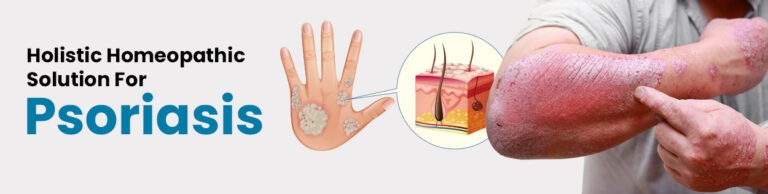
If you ever notice dry and scaly patches on your skin that cause itchiness, redness, and discomfort, then there is a possibility you might be affected by psoriasis. But what is this psoriasis disease?
In this blog, we will delve further into psoriasis disease and treatment for psoriasis. So please keep reading.
What is Psoriasis disease?
Psoriasis is a chronic skin disease or condition that is characterized by itchy, scaly, dry, and scaly patches on the skin. Psoriasis is an autoimmune condition where cells build up on the skin due to the rapid production of skin cells, thereby leading to scaly patches.
How common is psoriasis disease?
According to the National Psoriasis Foundation, 2-3% of the total world population of approximately 125 million are affected by psoriasis.
Prevalence of psoriasis disease in India
A study conducted in 2017 revealed that the prevalence rate of psoriasis skin disease in India is reported to be 0.44-28%. People affected were aged above 30-40 years, and men were affected two times more than women.
Who gets psoriasis?
Psoriasis disease is a common skin disease that can affect anyone, regardless of their age and their gender. However, this condition is commonly seen in adults.
What are the body areas affected by psoriasis?
Psoriasis skin rash can develop anywhere on the skin. However, some common body areas affected by psoriasis include the following,
- Face: Psoriasis on the face can be stressful and cause anxiety and low self-esteem in the patient. The effects of psoriasis on the skin include scaling, inflammation, and red patches.
- Inside the mouth: Oral psoriasis can present itself in the form of symptoms such as skin peeling on gums, pain and burning when eating, pus-filled blisters, mouth sores, red patches with white or yellow edges, etc.
- Hands: Psoriasis on hands and fingers can produce symptoms such as thick and raised skin, scaling with slivery white flakes, cracked skin, pain, itching, dryness, and bleeding.
- Fingernails: A person having psoriasis on nails may experience various symptoms such as dents or pits in the nails, nail crumbling, blood under the nails, yellow, white, or brown colored discoloration, separation of the nail from its bed, ridges in the nails, nail thickening, etc.
- Elbows: Individuals having psoriasis on the elbows may have symptoms such as a raised and inflamed patch, itching, pain, silver-colored scales, discoloration, etc.
- Toenails: A person having psoriasis on toenails may experience various symptoms such as nail crumbling, dents or pits on the nails, separation of the nail from its bed, blood under the nails, yellow or white or brown colored discoloration, ridges in the nails, nail thickening, etc.
- Knees: Psoriasis on the knees can present itself in symptoms such as skin itch, burning sensation, dryness on the skin, cracked skin, and red- or purple-colored patches with silver scales.
- Neck: Dry, raised patches, skin inflammation, and itchiness are common symptoms of psoriasis on neck skin.
- Scalp: Psoriasis on the scalp can cause symptoms such as a burning sensation, mild or severe itching, dry scalp, bleeding, cracked skin, flaking that resembles dandruff, thick red-colored patches on the scalp, etc.
- Palms: Patients with psoriasis on palms may have itching, cracked skin, pain, burning sensation, fissuring, etc.
- Genitals: Symptoms of genital psoriasis can manifest as skin itchiness, pain, skin dryness, cracked skin, pink or red to brown or purple colored discoloration of the skin, patchy skin, silver scales on shiny patches, and discomfort.
Types of Psoriasis:
There are five types of psoriasis. These five types of psoriasis include the following,
- Plaque Psoriasis
- Guttate Psoriasis
- Pustular psoriasis
- Inverse psoriasis
- Erythrodermic psoriasis
1. Plaque Psoriasis:
Plaque psoriasis is one of the most commonly occurring types of psoriasis. This type of psoriasis may appear anywhere on the body. In this type, red, inflamed patches on lighter skin tones and purplish or darker brown patches on the skin of color are seen. In individuals with skin of color, whitish-silver scales or plaques are common characteristics. Depending on the skin color of the individual, the color of the patches may differ.
The patches can exhibit color variations based on the individual’s skin tone, and the affected skin may undergo temporary changes in color during the healing process, especially on brown or Black skin (post-inflammatory hyperpigmentation). Plaque psoriasis is commonly seen on the,
- Scalp
- Knees
- Elbows
- Trunk
- Buttocks and extremities
2. Guttate Psoriasis:
Guttate Psoriasis is a type of psoriasis that is commonly seen in children and adolescents. This type of psoriasis is characterized by the development of symptoms such as small pink or violet spots on the skin. The spots appearing in this condition are distinct from the thick and raised plaques that are commonly seen in plaque psoriasis. Guttate Psoriasis can affect body regions such as,
- Arms
- Legs
- Torso
This type of psoriasis is often triggered by various conditions such as
- Tonsillitis
- Streptococcal infections
- Skin injuries
- Upper respiratory tract infections
- Stress
3. Pustular psoriasis:
Pustular psoriasis is a rare type of psoriasis that is seen more frequently in adults. This type of psoriasis is characterized by the formation of white, pus-filled blisters, along with wide areas of red and violet, depending on the color of the individual’s skin. Pustular psoriasis is not an infection, and hence, it is not contagious. This type of psoriasis can be widespread. Individuals with a darker skin tone are likely to have an intense violet color on their skin. In this type of psoriasis, the psoriasis is usually limited to small areas of the body, such as,
- Hands
- Feet
4. Inverse psoriasis:
Inverse psoriasis is commonly seen in individuals who are overweight or have deep skin folds. In inverse psoriasis, thin plaques without scales are formed. This type of psoriasis causes the formation of bright, shiny and inflamed skin with redness. Unlike plaque psoriasis, inverse psoriasis typically lacks the characteristic scales, resulting in smooth and shiny lesions. Due to the location of this type of psoriasis, the condition may worsen as a result of persistent irritation from skin rubbing and sweating. Inverse psoriasis patches are commonly seen affecting the skin folds found under,
- The breasts
- Armpits
- Groin
- Genital areas
5. Erythrodermic psoriasis:
Erythrodermic psoriasis is an intense and severe form of psoriasis affecting more than 90% of the skin. This type of psoriasis leads to widespread discoloration on the skin along with shedding. The affected area often resembles sunburn. The scales produced in this form tend to slough off in large sections or sheets.
Erythrodermic psoriasis is a life-threatening type of psoriasis that requires immediate medical attention. Erythrodermic psoriasis can disrupt the body’s chemical balance, leading to chronic complications such as congestive heart failure, edema, and pneumonia.
Individuals having erythrodermic psoriasis may experience symptoms such as,
- Inflammation
- Pain
- Severe itching in the affected areas
- Fever
Psoriasis and its severity:
Understanding the severity of psoriasis disease is crucial while navigating through the psoriasis journey. If you have psoriasis, then the treatment prescribed will vary typically based on the severity of the condition. Your healthcare provider will evaluate the severity of your condition by considering various factors. Based on the results of these factors, your psoriasis disease will be classified into mild, moderate or severe. The factors used to determine the severity of the condition include,
- The location and amount of skin affected
- The body’s surface area affected
- Intensity of the symptoms
- Impact of the condition on your everyday life
1. Mild Psoriasis:
Psoriasis symptoms developing on less than 3% of the body are considered as mild psoriasis. For reference, the size of our palm is 1% of the body. In the case of mild psoriasis, a few lesions will develop on the arms and legs. Additionally, a few patches may also develop on the scalp.
2. Moderate psoriasis:
When symptoms of psoriasis develop on about 3-10% of the body, then it is considered moderately severe psoriasis; in the case of moderate psoriasis, symptoms such as scaly red patches or dark-colored patches with thick silverish scales. Typically, if the psoriasis covers less than 3% of the body, it will still be considered moderately severe psoriasis if the symptoms develop on the genitals, palms, and face.
3. Severe psoriasis:
Psoriasis is said to be severe when its symptoms cover more than 10% of the body. The symptoms of severe psoriasis may develop in sensitive areas such as the soles of the palm or feet, nails, joints, etc. In addition to this, severe psoriasis also has a negative impact on the patient’s quality of life by affecting their daily life.
Causes of psoriasis disease:
Psoriasis skin disease is an autoimmune condition. In psoriasis disease, the immune system gets triggered, leading to the production of skin cells and their buildup in the form of plaques. Psoriasis disease is also hereditary and can sometimes be passed down to children from parents.
In normal conditions, it takes about 10-30 days for the skin cells to grow and get replaced. However, in the case of psoriasis disease, this cycle speeds up and the skin cells grow within 3-4 days. This quick process of skin replacement leads to the building up of skin cells and skin plaques are formed.
Triggers that lead to psoriasis flare-ups:
In patients having psoriasis disease, the condition may flare up when the immune system gets triggered and begins to fight and target the healthy cells in the body. Some common triggers that can cause flares in a person with psoriasis may include the following,
- Anxiety and stress
- Certain infections, such as streptococcal infections
- Hormonal changes in the body
- Changes in the body temperature due to cold or dry weather
- Skin injuries such as sunburns, cuts, scratches, bug bites or surgery
- Effect of certain medications such as beta-blockers, nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), antimalarial medicines, lithium, angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitors, etc.
Complications and Risks associated with Psoriasis:
Individuals with psoriasis disease may be affected by other health conditions as psoriasis may affect the muscles, bones, and the metabolic system. Individuals with psoriasis disease are at a risk of developing various health complications. Some of these health complications of psoriasis may include the following,
- Psoriatic arthritis can lead to joint pain, swelling and stiffness
- Eye conditions such as uveitis, conjunctivitis and blepharitis
- Mental health problems, such as stress, low self-esteem, anxiety and depression
- Post-inflammatory hyperpigmentation or post-inflammatory hypopigmentation
- Cardiovascular diseases
- Obesity
- Diabetes
- Certain types of cancers, such as lymphoma, lung cancer, and skin cancer (non-melanoma)
- Strokes
- High cholesterol levels
- Heart attacks
- High blood pressure
- Some other autoimmune conditions, such as sclerosis, celiac disease, or Crohn’s disease
Signs and Symptoms of psoriasis disease:
The signs and symptoms of psoriasis skin disease may vary from one patient to another depending on its type and location on the body. The symptoms of psoriasis may appear either on small areas of the body, such as the scalp, or even on most areas of the body.
Early signs of psoriasis
The appearance of small bumps that grow on the skin and have scales on their top is one of the early signs of psoriasis skin disease. Upon scratching, the scales may be removed from the skin and bleed. As these rashes persist to grow, they may form lesions.
Symptoms of psoriasis:
A person with psoriasis disease is likely to experience the following psoriasis symptoms,
- A rash or an area on the skin that is raised and thick
- Formation of plaque on the skin
- Scaly and flaky plaques
- Cracked, thick, or pitted nails
- Dry and cracked skin
- Bleeding on skin
- Joint swelling
- Skin itchiness
- Burning sensation around the patches
- Painful skin areas
- Pain in the joints
It is important to note that the severity of these psoriasis symptoms will vary from one individual to another, and not every patient will experience all of these symptoms.
Difference between seborrheic dermatitis and psoriasis:
Seborrheic dermatitis and psoriasis are two commonly occurring skin conditions. While both of these conditions are characterized by some common symptoms such as redness, flaking of the skin, and inflammation, they are still two distinct diseases. Some of the differences between the two conditions include:
| Seborrheic dermatitis | Psoriasis |
| The patches differ in color and can appear whitish-yellow, brown, or red in color. They also appear oily or greasy | Psoriasis is characterized by rough, red and scaly skin that becomes thick. Silverish-white-coloured scales are present on top of the patches. |
| The scales are less thick. | The scales are thicker. |
| Individuals will experience itchiness. | Individuals will experience itching along with pain. |
Difference between ringworm and psoriasis:
Psoriasis and ringworm are conditions affecting the skin. Both conditions can show up on about any part of the skin. Both conditions have some common symptoms such as redness and itchiness. However, they are two different skin problems and can easily be distinguished from each other through some of the below-mentioned differences:
| Ringworm | Psoriasis |
| It occurs as a result of fungal infection. | It is an autoimmune condition. |
| Ringworm is severely itchy and resembles a circular red rash with scaly borders. | Psoriasis is less itchy and looks like patches of red and raised skin covered with silver scales. |
| Ringworm infection is a temporary infection that can be removed with effective treatment. | Psoriasis is a lifelong condition. |
| Ringworm in most instances is seen on moist areas on the skin, such as the groin region, feet and near the beard. | Psoriasis can appear anywhere around the body but is commonly seen on the scalp, back, elbows, legs and knees. |
| Ringworm is highly contagious and can spread even from skin contact with an infected person. | Psoriasis is not contagious and cannot spread from a patient to a healthy person. |
Difference between dandruff and psoriasis:
Have you ever wondered if the itchiness in your scalp is due to something as simple as dandruff or is due to a concerning condition like psoriasis? The table will help you learn about the differences between dandruff and psoriasis to understand these scalp problems better.
| Dandruff | Psoriasis |
| In dandruff, flakes of small, dry skin pieces are seen on the scalp. | In psoriasis, the scalp will have itchy and painful red or sliver coloured patches. |
| In the case of dandruff, the person may not require medical attention. | Individuals with psoriasis need to seek professional help. |
| Dandruff may come and go from time to time. With proper hair care, it may not return for long. | Psoriasis is a life-long condition. |
| Dandruff is a mild form of a condition called seborrheic dermatitis. | Psoriasis is an autoimmune condition. |
Difference between eczema and psoriasis:
Eczema and psoriasis are two common skin conditions that can manifest in the form of symptoms such as discoloration on the skin, irritated skin, and inflammation. While some of its symptoms resemble, fortunately, there are certain differences in its appearance and some other symptoms that help diagnose it easily. The table shows us the differences between eczema and psoriasis.
| Eczema | Psoriasis |
| Eczema usually presents with red, inflamed skin that may be oozing, scaly, or crusty. Rough and leathery patches, sometimes appearing dark, are common, and swelling can also occur. | Psoriasis leads to red patches that may be silvery and scaly and appear as raised. |
| Individuals with eczema experience severe itching. | Psoriasis causes mild itching, along with stinging and burning. |
| Eczema usually develops in places with skin folds. | Psoriasis develops on the skin’s outer surfaces like the scalp or knees. |
| Eczema causes dry skin. | Psoriasis causes thick and raised plaques. |
Difference between psoriasis and fungal infection:
Psoriasis and fungal infection are skin issues characterized by the presence of red spots on the skin. While both fungal infection and psoriasis share some resemblances, they are two distinct conditions. Some of the differences setting these two conditions apart include:
| Fungal Infection | Psoriasis |
| Fungal infections are caused due fungi. | Psoriasis is an autoimmune condition. |
| Fungal infections occur due to overgrowth of fungus on the skin. | Psoriasis occurs due to the rapid overproduction of skin cells. |
| Fungal infections can occur anywhere but are mostly seen on moist body areas such as body folds, groin and feet. | Psoriasis can occur anywhere on the body, such as nails, knees, scalp, joints etc. |
| Fungal infections cause intense itching. | Psoriasis itching is lesser than fungal infections. |
| Fungal infections are contagious and can spread from the skin-to-skin contest. | Psoriasis is not contagious. |
Difference between psoriasis and lichen planus:
Have you ever wondered if a rash on your skin is psoriasis or lichen planus? Both psoriasis and lichen planus are two skin conditions that have some common features, such as a red scaly appearance. however, they also have some significant differences. a few such differences between psoriasis and lichen planus include:
| Lichen planus | Psoriasis |
| Lichen planus will have red bumps that will eventually go away on its own. | Psoriasis has thick patches that can stay on the skin for a long time. |
| Lichen planus is often seen affecting the lower back, wrists and ankles. | Psoriasis is often seen on elbows, knees, and scalp. |
| Lichen planus may clear up without any treatment about a year or more later. | Psoriasis is a life-long condition. |
Diagnosis of psoriasis disease:
Your healthcare provider or a dermatologist will diagnose the psoriasis skin condition. They will first conduct a thorough physical examination of your skin and ask you questions about your symptoms and their severity. Additionally, your doctor will also enquire about the medications, home remedies, and treatments done to relieve the symptoms.
Biopsy test:
If the symptoms and physical examination are unclear, then to confirm the condition of psoriasis, your doctor will collect a small sample of your skin for biopsy. A biopsy is usually done to confirm psoriasis, as its symptoms may sometimes resemble other conditions.
In a biopsy test, your doctor will apply or inject local anesthesia on the skin portion to be removed. As a result of anesthesia, the skin will become numb, making the procedure painless. Once the skin is removed, it is sent to a laboratory for analysis. This laboratory examination will help determine and confirm if you have psoriasis disease.
Psoriasis disease treatment:
Homeopathy treatment for psoriasis is gaining popularity with each passing day. This is because homeopathy treatment for psoriasis has minimal side effects, is safe, and also extremely reliable. Additionally, homeopathy treatment for psoriasis skin disorder is a suitable treatment option for patients of all ages.
A homeopathic doctor decides which homeopathy treatment for psoriasis is the best for you after studying your case thoroughly. Some commonly used homeopathy treatment options for psoriasis disease include the following,
When to see a Homeopathy Doctor for Psoriasis?
You can see a homeopathy doctor for psoriasis if you experience its symptoms and want to get a proper diagnosis. You can also see a homeopathic doctor if you have been diagnosed with psoriasis and want personalized homeopathic treatment for managing the symptoms and condition.
Side effects of psoriasis:
The various potential side effects and complications of psoriasis include the following,
- Psoriatic arthritis
- Cardiovascular problems
- Psychological Impacts, such as low self-esteem, depression, stress, and anxiety
- Infections
- Metabolic syndrome
- Eye problems
- Kidney problems
- Liver conditions
Home remedies for Psoriasis:
Various home remedies can help individuals with psoriasis get relief from symptoms of psoriasis. Some of these home remedies for psoriasis include the following,
Warm Baths:
Taking baths in lukewarm water can help in soothing the skin and itching. Additionally, it can also help with infiltration of plaques and scales. Adding mineral oils, oatmeal, olive oil, or Epsom salt can help in relieving the itching and irritation further.
Aloe vera:
Aloe vera plant has been used for treating skin problems and improving skin quality for years. Individuals with psoriasis can directly apply aloe vera gel from the plant to the psoriasis-affected skin. Aloe vera helps in reducing itching, discoloration of the skin inflammation, and scaling due to psoriasis.
Apple Cider Vinegar:
Studies have shown that applying apple cider vinegar can benefit individuals having scalp psoriasis. It can help ease itching and burning due to scalp psoriasis. For application, apple cider vinegar must be diluted with equal amounts of water. It is also essential to remember not to apply apple cider vinegar to broken or cracked skin.
Curcumin:
Found in turmeric, curcumin is very well known for its anti-inflammatory properties. Studies have found curcumin to be helpful in minimizing flare-ups of psoriasis and offering anti-inflammatory properties. It can be consumed in the form of supplements or pills or even added to foods. Before using turmeric for psoriasis, it is best to seek advice from a doctor.
Oregon grape:
Oregon grape is an antimicrobial herb. It is also known as Mahonia aquifolium. Certain studies have supported that using Oregon grapes can help patients with mild to moderate psoriasis.
Using Humidifiers:
Using humidifiers at home can prevent the skin from becoming dry. Excessive dryness can further irritate the psoriasis-affected skin. Hence, a humidifier can help ease the dryness of the skin by adding moisture to the air.
Using Moisturisers:
Psoriasis can cause skin itching, flaking, and dryness. To manage these symptoms, applying moisturizer can be beneficial. Moisturizers can be prescribed by a doctor and used along with other therapies. It is essential to note that moisturizers containing dyes and fragrances must be avoided, as they can irritate the skin further.
Relieving Stress:
One of the known triggers of psoriasis flare-ups is stress. Hence, reducing stress can help in preventing psoriasis flare-ups and also reduce their severity. To reduce stress, stress-relieving activities such as journaling, doing an activity we enjoy, meditating, performing yoga, aromatherapy, breathing exercises, etc can be helpful.
Diet for psoriasis:
Diet plays a vital role in managing the condition of psoriasis and preventing its complications. While a diet plays a crucial role in improving immune and body health, it is important to know that diet cannot cure psoriasis. Knowing which foods to add to the diet and which foods to avoid is important to manage psoriasis, prevent flare-ups, and reduce the severity of its symptoms.
Foods to Avoid while having Psoriasis:
Some foods that are to be avoided with psoriasis include the following,
- Gluten-rich foods: Certain research shows that individuals who have psoriasis are at a high risk of developing celiac disease. Individuals with celiac disease are intolerant to gluten, and hence, consuming it can cause inflammation lead to psoriasis flare-ups, and worsen its symptoms.
- Red meat: Red meat has high amounts of saturated fats and a type of polyunsaturated fatty acid known as arachidonic acid. This acid facilitates the production of compounds that increase inflammation in the body, thereby triggering psoriasis symptoms.
- Dairy: Studies have found that dairy products may contribute to inflammation in patients with psoriasis and trigger its symptoms. Hence, patients with psoriasis must avoid eating dairy.
- Processed foods: Eating processed foods can lead to more inflammation in the body. This may lead to flare-ups of psoriasis in the body. Additionally, processed foods also increase the risk of developing various other health conditions like obesity, heart problems, autoimmune conditions, and diabetes. etc.
- Alcohol: Alcohol has been linked to triggering symptoms of psoriasis in some patients. Alcohol affects the immune system pathways and triggers psoriasis symptoms.
- Foods with refined carbohydrates: Foods such as bread, white pasta, cakes, etc are high in sugar and carbohydrates. These foods increase inflammation and trigger psoriasis symptoms.
- Food containing trans fats and saturated fats (cheese and fried foods): Foods that are fried, such as fast foods, and cheese increase the amount of LDL (low-density lipoprotein in blood). These foods also increase inflammation in the body and worsen the symptoms of psoriasis.
- Foods high in sugar: Sodas, candies, pastries, fruit juices, etc in high quantities cause a spike in the inflammatory proteins known as cytokines in our body.
- Nightshades: Foods such as tomatoes, potatoes, peppers, and eggplant, contain solaine, which is reported to cause inflammation and trigger psoriasis flare-ups.
Foods to eat while having Psoriasis:
While some foods can trigger psoriasis and cause further inflammation, there are certain foods that, when added to the diet, can fight inflammation. Having a balanced diet with psoriasis is essential for managing the condition and overall health. Some foods that can be included in a psoriasis diet include the following,
- Fruits and vegetables: One of the best sources of anti-inflammatory foods is fruits and vegetables. They are rich in antioxidants that reduce oxidative stress and inflammation in the body. Individuals with psoriasis must include fruits and vegetables such as broccoli, leafy green vegetables, grapes, cherries, berries, cauliflower, etc in their diet.
- Nuts and seeds: Nuts and seeds are a source of various nutrients like omega-3 fatty acids, vitamins, minerals, antioxidants, fiber, etc, which help improve the immune and overall body health.
- Whole grains: Whole grains also contain various nutrients. Some whole grains such as oats also have anti-inflammatory properties and are fiber-rich which can help ease inflammation.
- Legumes: Legumes have various health benefits as they are rich in proteins, fibers etc. They also have anti-inflammatory properties and can help with easing inflammation.
- Fatty fish: Fatty fish has anti-inflammatory omega-3s in it. This helps in reducing the body’s over-inflammation.
- Oils supporting heart health: Heart-healthy oils such as olive oil, flax seed oil, coconut oil, and safflower oil contain anti-inflammatory fatty acids and help reduce inflammation.
- Supplements: Nutritional supplements such as Vitamin B12, Vitamin D, fish oil, etc, help in reducing inflammation in individuals with psoriasis. These supplements may also help in decreasing the severity of psoriasis flare-ups.
Individuals having psoriasis can also get a personalized diet prescribed by a dietician based on the problem.
Living with Psoriasis:
Living with psoriasis can be challenging. However, it is not impossible. With proper measures, treatment and following the doctor’s advice, psoriasis can be well managed. Certain measures that can help live with psoriasis include proper treatment, moisturizing skin, maintaining good personal hygiene, eating healthy meals, and practicing stress relieving techniques.
Additionally, to safeguard health and improve the quality of life, seeking help from mental health experts can also be beneficial. The risk of complications due to psoriasis can also be reduced by taking advice from a healthcare provider and properly following the prescribed measures.
If you are experiencing the symptoms of psoriasis or seeking personalized homeopathy treatment for psoriasis, then get in touch with us. Our team of experienced homeopathy doctors is here to help you with the management of psoriasis and improve the quality of your life. We provide accurate diagnosis and suitable treatment options based on your condition. Our homeopathic doctors will guide you in managing the condition effectively. So, don’t hesitate to schedule an appointment with us to address your concerns and improve your overall well-being.