Ever wondered why some girls and women go through unique challenges with their periods or notice changes in their bodies? Learn about PCOD, or Polycystic Ovary Disorder, a bit like a puzzle in the workings of the ovaries. PCOD can affect how these important parts of your body operate, leading to some differences.
This condition often involves tiny cysts on the ovaries, causing irregular periods and hormonal shifts. While the exact reasons aren’t crystal clear, factors like genetics and hormones play a role. Stick around as we learn everything about PCOD and understand how to manage it better.
What is PCOD? (PCOD Meaning)
Polycystic Ovary Disorder (or PCOD full form) in simple terms, it’s like a small hiccup in the usual way ovaries work. Normally, ovaries are like factories producing eggs, but with PCOD, tiny cysts (little sacs filled with liquid) can pop up on them, creating a bit of a stir.
This can lead to changes in your periods, making them a bit unpredictable. Sometimes, hormones can act a bit differently too. While the exact reasons for PCOD aren’t fully clear, things like family history and hormones seem to be part of the story. Understanding PCOD is like putting together the pieces of a puzzle, and we’re here to guide you through it.
How Common Is PCOD?
PCOD is quite common, affecting a significant number of girls and women. In fact, it’s one of the most prevalent hormonal disorders among people with ovaries. Estimates suggest that around 1 in 10 to 1 in 20 women of childbearing age can experience PCOD.
This means that you would know someone, whether a friend, family member or even yourself, who has dealt with or is dealing with a PCOD problem. It’s essential to recognize that while PCOD is common, its impact can vary from person to person. Some women experience mild symptoms of PCOD issues, while others can face more significant challenges. Understanding its prevalence helps shed light on the importance of awareness, early detection, and proper management.
Signs & Symptoms Of PCOD:
Ever felt like your body is trying to tell you something? Well, with PCOD, it’s like a secret message your body sends through signs. Let’s uncover these signals – from periods acting differently to changes in your skin and mood. Understanding the signs and symptoms of PCOD is like figuring out a puzzle, helping you know what your body could be going through. Let’s explore these signals together.
- Irregular Periods
- Hormonal Changes
- Weight Fluctuations
- Ovulatory Challenges
- Pelvic Pain
- Fatigue and Low Energy Levels
- Skin Discoloration
- Mood Changes
Irregular Periods:
PCOD can disrupt your menstrual cycle, causing periods to be irregular—coming too frequently, too infrequently, or sometimes not at all. This happens because the ovaries, responsible for releasing eggs, normally struggle with their usual routine due to hormonal imbalances.
Hormonal Changes:
Imbalances in hormones, especially elevated androgens, can lead to skin troubles like acne and changes in hair growth, such as increased facial or body hair. These changes occur as the body’s hormone levels get a bit mixed up, impacting the skin and hair.
Weight Fluctuations:
PCOD is often linked to weight concerns. Some normally find it hard to manage weight, while others can experience unexplained weight gain. This happens because PCOD can affect how the body uses insulin, influencing both weight and hormonal balance.
Ovulatory Challenges:
Disruptions in the ovulation process can create difficulties in getting pregnant or lead to fertility issues. This occurs because PCOD affects the regular release of eggs from the ovaries, impacting fertility.
Pelvic Pain:
Experience of discomfort or pain in the pelvic region is another possible symptom of PCOD. This happens because the cysts on the ovaries can cause physical discomfort.
Fatigue and Low Energy Levels:
PCOD can contribute to feelings of fatigue and low energy. Managing energy levels becomes more challenging, underscoring the impact of PCOD on overall well-being. This occurs due to the hormonal imbalances affecting the body’s energy regulation.
Skin Discoloration:
Dark patches of skin, especially around the neck, groin, or under the breasts, can occur due to insulin resistance—a notable feature often seen in individuals with PCOD. Insulin resistance affects the skin’s pigmentation.
Mood Changes:
Hormonal fluctuations in PCOD can influence mood. Mood swings, anxiety, or depression can manifest as part of the emotional toll associated with this condition. These mood changes are linked to the hormonal shifts affecting the brain’s chemistry.
Recognizing these signs is crucial for early detection and effective management of PCOD problems, as each symptom provides valuable clues about how the condition is impacting different aspects of the body.
Causes Of PCOD:
Ever wondered what could be the causes of PCOD? It’s like uncovering the secrets behind a puzzle. Let’s explore the factors – from family links to hormone mix-ups – that give us clues about why PCOD generally shows up.
- Genetic Influence
- Hormonal Imbalances
- Insulin Resistance
- Inflammation
- Lifestyle Factors
- Weighted
- Environmental Influences
- Puberty Onset

Genetic Influence:
PCOD can have a genetic component, meaning it can run in families. If someone in your family has PCOD, there’s an increased likelihood that you can be more predisposed to developing it too. Understanding family history is crucial in assessing the potential risk of PCOD.
Hormonal Imbalances:
PCOD involves a hormonal mix-up, particularly with androgens (male hormones), such as testosterone and DHEA. When these hormones become imbalanced, it can impact the normal functioning of your ovaries, contributing to the development of PCOD. This hormonal disruption can lead to symptoms like irregular menstrual cycles, acne, and hirsutism.
The elevated levels of androgens in PCOD can interfere with the regular release of eggs during the menstrual cycle, causing irregular periods. Additionally, the hormonal imbalance may contribute to the formation of ovarian cysts, further complicating the condition. Understanding and addressing these hormonal imbalances is crucial for managing the symptoms and promoting overall reproductive health in individuals with PCOD.
Insulin Resistance:
Insulin resistance is a key player in PCOD. Insulin often likened to a key that helps the body use sugar for energy, faces resistance in individuals with PCOD. This resistance causes higher insulin levels, which, in turn, can impact hormonal balance and play a significant role in the development of PCOD.
Inflammation:
Inflammation, characterized by small swellings in the body, is linked to PCOD. This inflammation can influence how your ovaries function, contributing to the development of PCOD. Addressing inflammation is an important aspect of managing PCOD.
Lifestyle Factors:
Your lifestyle choices matter in the context of PCOD. Factors like a diet high in refined sugars and a lack of physical activity could contribute to the development or worsening of PCOD symptoms. Adopting a healthy lifestyle with a balanced diet and regular exercise can positively impact PCOD management.
Weight:
There’s a cyclical relationship between PCOD and weight. PCOD can make it challenging to manage weight, and being overweight can make PCOD symptoms more pronounced. Maintaining a healthy weight through lifestyle modifications is beneficial for managing PCOD.
Puberty Onset:
PCOD often becomes noticeable during puberty. Changes in hormones and the menstrual cycle during this time can trigger or reveal the presence of PCOD. Monitoring and addressing symptoms during puberty are crucial for early intervention and management.
Understanding these factors provides a clearer picture of PCOD’s roots. It’s like putting together the pieces of a puzzle, helping both individuals and healthcare professionals address and manage PCOD problems effectively.
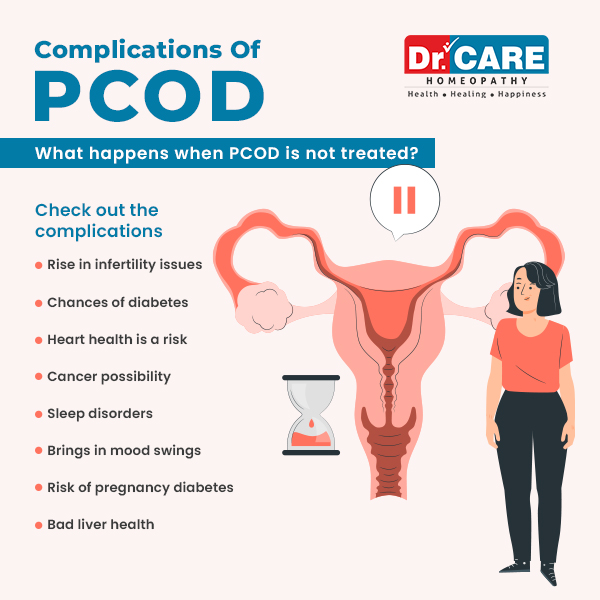
Complications Of PCOD:
Polycystic Ovary Disorder (PCOD) can bring about various complications that can impact different aspects of your health. Here are some potential complications associated with PCOD:
- Infertility
- Type 2 Diabetes
- Cardiovascular Issues
- Endometrial Cancer
- Sleep Apnea
- Mood Disorders
- Gestational Diabetes
- Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (NAFLD)
Infertility:
Irregular ovulation in PCOD means that eggs would not be released regularly, making it challenging for individuals to conceive. Hormonal imbalances disrupt the typical ovulation process, contributing to fertility issues.
Type 2 Diabetes:
PCOD is often linked to insulin resistance, where the body’s cells don’t respond well to insulin. This can lead to higher levels of insulin and, eventually, an increased risk of developing type 2 diabetes as the body struggles to regulate blood sugar effectively.
Cardiovascular Issues:
Elevated insulin levels, along with other factors like high blood pressure and abnormal cholesterol levels, can contribute to cardiovascular problems. These issues are associated with insulin resistance and the overall metabolic impact of PCOD.
Endometrial Cancer:
Irregular or absent menstrual cycles mean that the uterine lining (endometrium) could be exposed to higher levels of estrogen without regular shedding during menstruation. This prolonged exposure increases the risk of endometrial cancer over time.
Sleep Apnea:
Hormonal imbalances and obesity, often associated with PCOD, can contribute to the development of sleep apnea. Changes in body composition and the impact of hormones can lead to disruptions in breathing during sleep.
Mood Disorders:
Hormonal fluctuations in PCOD can influence mood. The challenges of living with PCOD, managing symptoms, and potential fertility concerns could contribute to mood disorders like anxiety and depression.
Gestational Diabetes:
Women with PCOD problems have an increased risk of developing gestational diabetes during pregnancy. This is likely due to the underlying insulin resistance that is common in PCOD.
Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (NAFLD):
Insulin resistance associated with PCOD can lead to the accumulation of fat in the liver, contributing to non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. Regular monitoring of liver health is crucial to address and manage this potential complication.
Understanding the origins of these complications emphasizes the importance of a holistic approach to PCOD management, involving lifestyle modifications, regular monitoring, and collaboration with healthcare professionals.
Difference Between PCOD vs PCOS:
Generally, women get confused with PCOD and PCOS. Many women also think that both of these issues are the same. However, we have the five key differences between PCOD (Polycystic Ovary Disorder) and PCOS (Polycystic Ovary Syndrome):
| Sno | PCOD | PCOS |
| Definition | Refers to ovaries with multiple small cysts, primarily focusing on the ovarian morphology. | Encompasses both the presence of ovarian cysts and additional hormonal and metabolic imbalances, forming a syndrome. |
| Effect | Polycystic Ovary Disorder (PCOD) is a widespread condition, affecting about 10% of women globally. | Polycystic Ovary Syndrome (PCOS), on the other hand, is a more severe medical condition, with an incidence ranging from 0.2% to 2.5% among women worldwide. |
| Scope of Involvement | Primarily describes the appearance of the ovaries, with or without associated symptoms. | Involves a broader range of factors, including irregular menstrual cycles, elevated androgen levels, and potential metabolic issues. |
| Diagnosis Criteria | Diagnosed through ultrasound images revealing multiple cysts on the ovaries. | Diagnosis involves meeting specific criteria, including ovarian cysts, irregular periods, and elevated androgen levels. |
| Symptoms | May or may not be associated with symptoms like irregular periods, acne, and hair growth. | Typically presents with a range of symptoms, including irregular menstrual cycles, acne, hirsutism (excessive hair growth), and potential fertility issues. |
| Clinical Implications | Often considered a milder form with fewer associated health risks. | Has broader clinical implications, potentially leading to fertility challenges, metabolic issues, and an increased risk of conditions like diabetes and cardiovascular diseases. |
While PCOD primarily focuses on the appearance of the ovaries, PCOS encompasses a wider spectrum of hormonal and metabolic imbalances, accompanied by a more extensive set of symptoms and potential health risks. At Dr Care Homeopathy, we treat both PCOD and PCOS.
Diagnosis of PCOD:
Getting to the bottom and understanding the diagnosis of PCOD involves several steps to know what’s happening in your body. Here’s a closer look at how doctors typically go about it:
- Medical History
- Physical Exam
- Blood Tests
- Ultrasound
- Excluding Other Conditions
- Menstrual Cycle Tracking
- Symptom Assessment

Medical History:
Gathering your medical history allows your healthcare provider to understand patterns, symptoms, and potential risk factors related to PCOD. This information helps in identifying key aspects of your health that can be indicative of PCOD.
Physical Exam:
A physical examination provides tangible evidence of PCOD-related changes, such as skin and body weight variations. Visual cues during the exam contribute to the overall understanding of how PCOD could be manifesting physically.
Blood Tests:
Blood tests are essential for quantifying hormone levels, including androgens and insulin. Elevated levels of these hormones are characteristic of PCOD, and blood tests help in confirming these imbalances, aiding in a more accurate diagnosis.
Ultrasound:
An ultrasound offers a visual confirmation of the presence of small cysts on the ovaries, a key feature of PCOD. It provides direct insight into the structural changes within the reproductive organs, strengthening the diagnostic process.
Excluding Other Conditions:
Ruling out other conditions with similar symptoms ensures that the diagnosis is specific to PCOD. It helps in avoiding misdiagnosis and guides healthcare providers toward appropriate management strategies.
Menstrual Cycle Tracking:
Monitoring your menstrual cycles is crucial as irregular periods are a common symptom of PCOD. This information aids in understanding the cyclical hormonal changes, contributing to the overall diagnostic picture.
Symptom Assessment:
Discussing your symptoms provides a holistic perspective on how PCOD is impacting various aspects of your health. It helps healthcare providers tailor their approach to address specific concerns and symptoms you could be experiencing.
Combining these puzzle pieces helps your doctor form a comprehensive understanding. If PCOD is suspected or confirmed, they can work with you to create a tailored plan for managing the condition. Regular follow-ups and additional tests can be recommended to monitor your health over time. Remember, the diagnosis process is about uncovering the unique aspects of your health journey.
Lifestyle modification
While it’s not always possible to prevent PCOD, certain lifestyle choices can help manage symptoms and reduce the risk of complications. Here are key strategies for potentially preventing or mitigating PCOD:
- Maintain a Healthy Weight
- Regular Physical Activity
- Balanced Diet
- Regular Check-ups
- Manage Stress
- Limit Processed Foods
- Avoid Smoking and Excessive Alcohol
- Birth Control Pills

Maintain a Healthy Weight:
Aim for a balanced and healthy weight. Weight management can positively influence hormonal balance and reduce the risk of insulin resistance, a common factor in PCOD. Managing a healthy weight is crucial because excess body fat can lead to insulin resistance, a common factor in PCOD. Maintaining a balanced weight helps regulate insulin levels, potentially reducing the risk of PCOD problems.
Regular Physical Activity:
Engage in regular PCOD exercise to support overall health. Exercise is beneficial for weight management, improving insulin sensitivity, and promoting hormonal balance. Regular physical activity can contribute to a healthier overall profile, reducing the likelihood of developing PCOD problem.
Balanced Diet:
Adopt a balanced and nutritious diet. Focus on whole foods, fruits, vegetables, and lean proteins while minimizing processed foods and sugars. A healthy diet supports overall well-being and can help regulate hormones. A balanced diet supports overall health and helps regulate hormones. Whole foods, fruits, vegetables, and lean proteins contribute to a stable hormonal environment, potentially preventing or managing PCOD.
Regular Check-ups:
Schedule regular check-ups with your healthcare provider. Early detection and intervention can help manage PCOD more effectively, preventing complications and promoting overall health. Regular check-ups with healthcare providers allow for early detection and intervention. Monitoring health parameters enables timely management of PCOD and reduces the risk of complications.
Manage Stress:
Practice stress-reducing activities such as yoga, meditation, or deep breathing exercises. Chronic stress can impact hormone levels and exacerbate PCOD symptoms. Chronic stress can impact hormone levels, exacerbating PCOD symptoms. Stress-reducing activities help maintain hormonal balance and mitigate the effects of stress on the body.
Limit Processed Foods:
Reduce the intake of processed and high-sugar foods. These can contribute to insulin resistance and weight gain, potentially worsening PCOD symptoms. Processed and high-sugar foods contribute to insulin resistance and weight gain. By limiting these foods, individuals can better manage insulin levels and decrease the risk of PCOD-related complications.
Avoid Smoking and Excessive Alcohol:
Smoking and excessive alcohol consumption can impact hormonal balance. Smoking and excessive alcohol consumption can disrupt hormonal balance. Avoiding these substances supports overall hormonal health, potentially reducing the risk of developing PCOD.
Birth Control Pills:
In some cases, birth control pills can be recommended to regulate menstrual cycles and hormones. In some cases, birth control pills could be prescribed to regulate menstrual cycles and hormones. This can help manage mild PCOD symptoms effectively under the guidance of a healthcare professional. Consult with your healthcare provider to discuss whether this option is suitable for you.
These prevention strategies aim to create a supportive environment for hormonal balance and overall health, reducing the risk of PCOD or mitigating its impact. Adopting a holistic approach to health can be instrumental in preventing and managing PCOD.
Diet Plan For PCOD:
Creating a diet plan for Polycystic Ovary Disorder (PCOD) involves focusing on nutrient-dense foods that help regulate insulin levels, manage weight, and support overall hormonal balance. Here are 10 informational pointers for a PCOD-friendly diet plan:
Whole Grains:
Incorporate whole grains like oats, quinoa, brown rice, and whole wheat bread. These provide complex carbohydrates, fiber, and essential nutrients, promoting steady blood sugar levels and aiding in weight management.
Lean Proteins:
Include lean protein sources such as skinless poultry, fish, tofu, legumes, and lentils. These protein-rich foods support muscle health, regulate appetite, and stabilize blood sugar levels.
Fruits and Vegetables:
Opt for a variety of colorful fruits and vegetables, including leafy greens, berries, citrus fruits, apples, carrots, and broccoli. These provide antioxidants, vitamins, minerals, and fiber, supporting overall health and hormonal balance.
Healthy Fats:
Incorporate sources of healthy fats like avocados, nuts, seeds, and olive oil. These fats provide essential fatty acids, promote satiety, and support hormone production and balance.
Low-Glycemic Index Foods:
Choose low-glycemic index foods such as sweet potatoes, legumes, and non-starchy vegetables. These foods release sugar into the bloodstream slowly, preventing spikes in blood sugar levels and improving insulin sensitivity.
Probiotic-Rich Foods:
Consume probiotic-rich foods like yogurt, kefir, and fermented vegetables. Probiotics support gut health, aid in digestion, and may help alleviate gastrointestinal symptoms associated with PCOD.
Anti-Inflammatory Foods:
Incorporate anti-inflammatory foods such as fatty fish (salmon, mackerel), turmeric, ginger, garlic, and green tea. These foods help reduce inflammation, which is often elevated in individuals with PCOD.
Hydrating Beverages:
Stay hydrated with water, herbal teas, and infused water. Proper hydration supports digestion, helps regulate hormone levels, and promotes overall health.
Moderate Amounts of Dairy:
Include moderate amounts of dairy products such as milk, yogurt, and cheese. Opt for low-fat or skim options and consider choosing hormone-free or organic dairy products to minimize potential hormonal disruptions.
Portion Control and Balanced Meals:
Practice portion control and aim for balanced meals containing a combination of carbohydrates, proteins, and fats. Eating balanced meals helps regulate blood sugar levels, control appetite, and maintain overall energy levels.
Remember to consult with a healthcare professional or a registered dietitian to personalize this diet plan according to individual needs and preferences. Additionally, regular physical activity, stress management, and adequate sleep are essential components of a holistic approach to managing PCOD.
Food To Avoid During PCOD:
Avoiding certain foods can help manage symptoms associated with Polycystic Ovary Disorder (PCOD). Here are specific foods to consider limiting or avoiding:
Highly Processed Foods:
Steer clear of heavily processed foods, commonly found in fast food and pre-packaged meals. These foods often contain preservatives, artificial additives, and unhealthy trans fats, all of which can contribute to inflammation and exacerbate insulin resistance, common concerns in PCOD.
Sugary Foods and Beverages:
Limit or avoid sugary snacks, candies, pastries, and sweetened beverages. Excessive sugar intake can lead to not only rapid blood sugar spikes but also increased cravings and energy crashes, impacting overall hormonal balance and making weight management more challenging for individuals with PCOD.
Refined Carbohydrates:
Minimize consumption of refined carbohydrates like white bread and sugary cereals. These foods have a high glycemic index, leading to quick spikes in blood sugar levels, which can contribute to insulin resistance, a key factor in PCOD.
Highly Saturated Fats:
Reduce intake of foods high in saturated fats, such as fried foods and fatty cuts of meat. Saturated fats can contribute to inflammation and hormonal imbalances, potentially worsening symptoms associated with PCOD.
Dairy with Added Hormones:
Consider limiting or choosing hormone-free dairy products to avoid potential disruptions to hormonal balance. Some conventionally produced dairy products can contain added hormones, which could impact the endocrine system
Excessive Caffeine:
Cut back on excessive caffeine intake, especially from high-caffeine energy drinks and coffee. While moderate caffeine consumption could be acceptable, excessive amounts can disrupt cortisol levels, potentially influencing hormonal balance in individuals with PCOD.
Alcohol:
Limit alcohol consumption, particularly sugary cocktails and excessive intake. Alcohol can impact liver function, affecting hormonal balance and potentially worsening PCOD symptoms. Moderation is key to minimizing these effects.
Highly Salted Foods:
Minimize consumption of highly salted foods, such as processed snacks and canned soups. High sodium intake can contribute to bloating and hypertension, impacting overall well-being, and potentially exacerbating PCOD symptoms.
Soy-Based Products:
Consider moderating intake of soy-based products, which contain phytoestrogens. While soy has health benefits, excessive consumption can interfere with hormonal balance, affecting individuals with PCOD differently.
Trans Fats:
Avoid foods containing trans fats, often found in partially hydrogenated oils. Trans fats can contribute to inflammation and insulin resistance, both of which are concerns in PCOD. Checking ingredient labels for partially hydrogenated oils helps identify and eliminate these harmful fats from the diet.
It’s important to note that individual responses to foods can vary, and not all individuals with PCOD will need to avoid these foods entirely. Consultation with a healthcare professional or a registered dietitian is recommended to create a personalized dietary plan that aligns with individual health needs and goals. Additionally, adopting a balanced and whole-food-based diet is generally beneficial for managing PCOD symptoms.
PCOD Treatment:
The treatment approach for Polycystic Ovary Syndrome (PCOD) is typically multifaceted and aims to manage symptoms, regulate hormonal imbalances, and address potential long-term health risks. Here are common components of PCOD treatment:
- Lifestyle Modifications:
- Medications
- Fertility Treatments
- Weight Management
- Nutritional Guidance
- Regular Monitoring and Follow-up
- Psychological Support
- Management of Specific Symptoms
- Homeopathic Treatment
Lifestyle Modifications:
Adopting a healthy lifestyle is often the first line of treatment. This includes regular PCOD exercise, a balanced diet rich in whole foods, and maintaining a healthy weight. Lifestyle modifications can improve insulin sensitivity, regulate menstrual cycles, and alleviate symptoms such as excessive hair growth and acne.
Medications:
Various medications can be prescribed based on specific symptoms and individual needs. Common medications include oral contraceptives, anti-androgen medications, and insulin-sensitizing drugs. Oral contraceptives help regulate menstrual cycles and reduce androgen levels. Anti-androgen medications address symptoms like hirsutism, while insulin-sensitizing drugs can improve insulin resistance.
Fertility Treatments:
For individuals trying to conceive, fertility treatments can be recommended. This can include ovulation-inducing medications or assisted reproductive technologies such as in vitro fertilization (IVF). These treatments aim to stimulate ovulation and increase the chances of successful conception.
Weight Management:
Achieving and maintaining a healthy weight is crucial for managing PCOD symptoms, especially those related to insulin resistance. Weight loss can improve insulin sensitivity, regulate menstrual cycles, and reduce the severity of other symptoms associated with PCOD.
Nutritional Guidance:
Working with a registered dietitian can provide personalized nutritional guidance. This can include recommendations for a balanced diet, managing carbohydrate intake, and addressing specific nutritional needs. Proper nutrition can support overall health, manage weight, and address specific concerns related to insulin resistance and hormonal imbalances.
Regular Monitoring and Follow-up:
Regular check-ups with healthcare providers are essential for monitoring symptoms, adjusting treatment plans, and addressing any emerging health concerns. Continuous monitoring ensures that treatment plans are effective and allows for timely adjustments based on individual responses.
Psychological Support:
PCOD can have emotional and psychological impacts. Counseling or support groups could be beneficial for addressing mental health concerns and improving overall well-being. Emotional support can help individuals cope with the challenges associated with PCOD, promoting mental and emotional health.
Management of Specific Symptoms:
Targeted treatments can be recommended to manage specific symptoms, such as acne, excessive hair growth (hirsutism), or hair loss. These treatments address cosmetic concerns and improve the quality of life for individuals with PCOD.
Homeopathic Treatment:
Homeopathy is a form of alternative medicine that involves using highly diluted substances to stimulate the body’s natural healing processes. Homeopathic treatments for PCOD could include remedies tailored to individual symptoms and constitutional factors. Homeopathic practitioners typically conduct a detailed assessment of the individual’s symptoms, lifestyle, and overall health to prescribe personalized homeopathic remedies. These remedies can include substances like Pulsatilla, Sepia, or Lachesis, depending on the specific presentation of symptoms.
Treatment plans are individualized, and healthcare providers work closely with patients to tailor interventions based on specific symptoms, reproductive goals, and overall health. The primary goal is to enhance quality of life, manage symptoms effectively, and reduce the risk of long-term health complications.
Dr Care Homeopathy Clinic For PCOD:
At Dr. Care Homeopathy Clinic, we take pride in being your dedicated destination for top-notch PCOD care. Our team comprises experienced homeopathic doctors, each boasting over three decades of expertise, ensuring a commitment to patient-centric treatment, even in challenging cases.
Discover the distinctive Dr. Care Homeopathy approach as you initiate a journey toward healing and enhanced well-being with our seasoned team. Whether you’re grappling with mild discomfort or seeking solutions for complex cases, our clinic provides tailored and expert care, empowering you to regain control over your life. Experience the excellence of Dr. Care Homeopathy Clinic, where our focus on personalized and compassionate care makes us a reliable choice for effective PCOD treatment.